Green Shipping Innovations: How the Maritime Industry is Reducing Its Carbon Footprint

The maritime industry is key to global trade, carrying 90% of it. It’s also a big emitter, responsible for 2-3% of greenhouse gases. To cut down, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) wants to reduce emissions by at least 50% by 2050.
The UK is at the forefront of making maritime transport greener. It’s investing £206 million in the UK SHORE programme to clean up the sector. A part of this, £9 million, will go to the Green North Sea Shipping Corridor Project. This project hopes to cut 850,000 tonnes of CO2 every year.
The Clean Maritime Demonstration Competition (CMDC) has given over £128 million to 138 projects. These projects are all about making shipping greener. The UK wants to be a leader in zero-carbon shipping, with the sector set to grow to £13 billion by 2030.
There are many ways to make shipping greener, like using wind or new fuels like hydrogen and ammonia. These changes are good for the planet and could also be very profitable. The market for these green technologies is expected to grow to USD 9.5 billion by 2025.
Key Takeaways
- The maritime industry aims to reduce emissions by 50% by 2050
- UK SHORE programme allocates £206 million for maritime decarbonisation
- Green North Sea Shipping Corridor Project targets 850,000 tonnes of CO2 savings annually
- Clean Maritime Demonstration Competition funds 138 innovative projects
- UK shipping technology sector projected to reach £13 billion annually by 2030
- Global green shipping technology market expected to hit USD 9.5 billion by 2025
The Importance of Green Shipping Innovations
The maritime industry must cut its environmental harm. Almost 90 percent of global goods travel by sea. This makes eco-friendly ship tech more urgent than ever.
The sector’s carbon footprint is huge. It uses 300 million tons of fuel each year. This adds up to about 3% of all global carbon dioxide emissions.
Understanding Carbon Footprint in the Maritime Sector
Ships use a lot of fuel, with big ones burning up to 300 metric tons daily. This leads to big emissions and health problems. New ship designs are key to solving these problems:
- Speed nozzles can save about 5% in fuel consumption
- Anti-fouling hull paint reduces fuel use by 3-8%
- Waste heat recovery systems convert exhaust gases into steam
- Submarine robot cleaners decrease fuel consumption by 20-40%
The Role of Government Regulations
Government rules are vital for green shipping. The International Maritime Organization’s 2020 sulphur cap is a big step. It means all ship fuels must have less than 0.50% sulphur.
This rule will help reduce health risks. It’s expected to cut premature deaths by 34% and illnesses by 54%.
To follow these rules, the industry is exploring new tech. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is one option. It cuts sulphur oxide emissions by nearly 100% and nitrogen oxide by up to 90%.
Ship design is changing fast. New ideas like rotor sails could cut fossil fuel use by 20%.
“Green shipping is not just an environmental imperative; it’s becoming a business necessity in the face of tightening regulations and increasing public awareness.”
Key Technologies Driving Green Shipping
The maritime industry is working hard to cut its carbon footprint. Shipping is responsible for 2.3% of global CO2 emissions. New technologies are key to making ships greener.
Alternative Fuels: LNG and Beyond
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is becoming a popular choice. The industry is also looking into biofuels, ammonia, and hydrogen. The Stamford Eagle cut its carbon emissions by 80% with biofuels.
Energy Efficiency Measures on Vessels
Speed nozzles are changing how ships move. They can save about 5% of fuel compared to old systems. The industry has cut carbon emissions by 40% from 2008 to 2018. This is thanks to better designs and technology.
Advances in Maritime Engineering
New propulsion systems are leading the way in ship design. Air lubrication tech, despite challenges, could save a lot of fuel. Better hull designs and energy-saving tech are also helping to reduce emissions.
“The transition to alternative fuels is expected to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution within the shipping sector.”
The International Maritime Organization aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50% by 2050. This goal is pushing for fast progress in green ship technology.
The Impact of Renewable Energy in Shipping
Renewable energy is changing the maritime world. It’s leading to green shipping routes and zero-emission ships. The shipping sector, which emits 2% to 3% of all carbon, must cut CO2 by 45% by 2030 to meet climate targets.
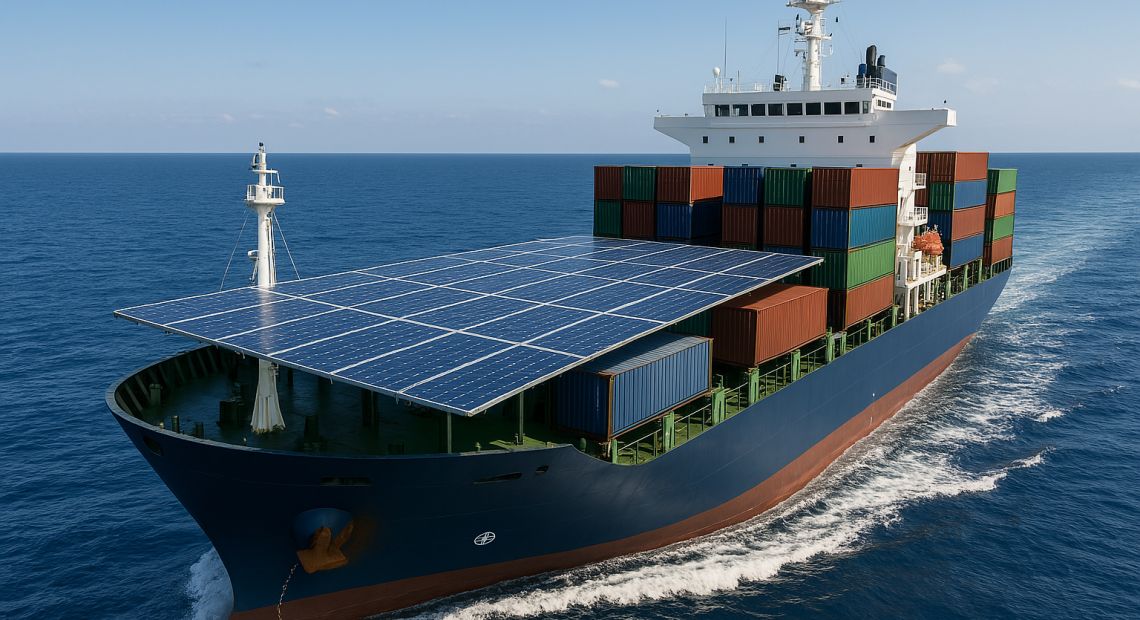
Solar Panels Installation on Cargo Ships
Solar tech is becoming more common in shipping. Big cargo ships are adding solar panels to help power them. These panels cut down on fuel use, mainly for electrical systems.

Though they can’t power ships alone, solar panels help lower emissions. This is key for green shipping routes.
Wind-Assisted Propulsion Systems
Wind power is back in shipping. A.P. Moller-Maersk A/S is testing advanced sails on its ships. These sails, made by Norsepower Oy Ltd., could cut fossil fuel use by up to 20%.
FastRig technology also uses wind to reduce fuel use by about 30% a year. This depends on the route, speed, and ship size.
With 40,000 ships that could use wind tech, the emissions reduction is huge. These new methods are vital for reaching net zero emissions by 2040. They’re helping create zero-emission vessels and green shipping corridors worldwide.
The Role of Digitalisation in Green Shipping
Digitalisation is changing the maritime world. It’s making shipping more sustainable and eco-friendly. Smart technologies and data analytics are making ships work better, saving energy and reducing harm to the environment.
Smart Shipping Technologies
Smart shipping tech is leading the way in maritime innovation. It helps ships run better, use less fuel, and pollute less. For example, wind-assisted systems can cut fuel use by 3% to 15%, making ships greener.
Real-time Monitoring and Data Analytics
Real-time monitoring and data analytics are key for better shipping. They help track how much fuel ships use and how well they perform. This lets companies make smart choices to save energy and cut emissions.
“New technologies for greener shipping” – World Maritime Day 2022 theme, emphasising the importance of innovation in the maritime sector.
Digitalisation is also changing ship design. Battery hybrids are being used to make ships more energy-efficient. This is a big step towards the European Green Deal’s goal of cutting transport emissions by 90% by 2050.
The maritime industry is getting greener with digitalisation. New tech is helping ships use less fuel and handle cargo better. These changes are taking the industry towards a cleaner future.
Case Studies of Successful Green Shipping Initiatives
The maritime industry is moving towards sustainability fast. Big names are leading the way. Let’s look at how two giants are using eco-friendly tech and biofuels to cut down on carbon.
Maersk’s Sustainability Strategy
Maersk Line, a top container shipper, is making big strides in green shipping. They use data to find the best routes, cutting down fuel use and emissions. This move is good for the planet and saves them money too.

CMA CGM’s Commitment to Eco-friendly Practices
CMA CGM is all in on eco-friendly shipping, focusing on biofuel ships. They’ve bought vessels that can run on cleaner fuels, cutting down carbon emissions a lot.
The Stamford Eagle’s journey is a great example. In December 2022, it sailed from the Netherlands to Norway on biofuels. It cut carbon emissions by 80% for that trip.
These stories show the real benefits of green shipping. Maersk and CMA CGM are showing the way with their green tech and fuels. They’re making the maritime world more sustainable.
Collaborations and Partnerships in the Industry
The maritime sector is making big steps towards green shipping thanks to partnerships. Shipping is responsible for 3% of global CO2 emissions. Leaders are coming together to solve this environmental problem.
Industry Alliances for Sustainable Shipping
Big names in the maritime world are forming strong alliances. They aim to make shipping cleaner. The Maersk Mc-Kinney Moller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping, with 24 partners, is leading this effort. They want to make shipping net-zero by 2050.
The International Association of Ports and Harbors (IAPH) has brought together 100 ports globally. They’re working on innovation and sustainability. This is key for green shipping across the world.
Role of NGOs in Promoting Green Innovations
Non-governmental organisations are key in making shipping sustainable. Ocean14 has set up a $200 million fund for the blue economy. They focus on sustainable fishing and plastic recycling, helping marine conservation.
Green Marine offers a plan for companies to reduce their environmental impact. They tackle pollution in air, land, and water. This sets new standards for the industry.
- 13 maritime industry representatives signed a declaration at the Hamburg Sustainability Conference
- The Port of Barcelona’s Blue Tech Port project spans 25,000 square feet
- The Port Innovation Network (PIN) was established by Ports of Hamburg, Halifax, and Valencia
These partnerships are pushing for new fuels, wind-assisted ships, and smart ports. They’re working towards a greener future for global shipping.
The Future of Maritime Sustainability
The maritime industry is on the verge of a green revolution. As global trade grows, it must cut its environmental harm. Shipping is responsible for nearly 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making new solutions essential.
Emerging Trends in Green Shipping Innovations
Zero-emission vessels are becoming a reality, not just a dream. The sector is seeing a lot of research into clean energy. Green hydrogen, made from renewable energy, is seen as a key fuel for net-zero emissions.
Wind-assisted propulsion is back, with new technologies. Modern sail systems are being added to cargo ships, cutting fuel use. The Grain de Sail II cargo ship is a good example, following strict EU rules.
Predictions for the Next Decade
The International Maritime Organization wants a 40% efficiency boost by 2030 and a 50% cut in emissions by 2050. We can look forward to:
- More use of alternative fuels like biofuels, methanol, and ammonia
- More investment in wind-assisted propulsion
- Better hull designs and propellers for less fuel use
- More ‘Green Corridors’ between major ports
The maritime industry is moving towards a greener future. With more zero-emission vessels and better wind-assisted propulsion, it’s set for a cleaner, more efficient era.
Challenges Facing the Adoption of Green Technologies
The maritime industry is on a journey to become more sustainable. It needs low-emission systems and green logistics. But, there are big obstacles in the way.
Financial Barriers to Innovation
Green technologies are expensive, which is a big problem. Shipowners are hesitant to spend money on new systems. For example, making half of all containerships run on ammonia could cost £59 billion.
Resistance to Change in Traditional Practices
The shipping sector is slow to change. Only 0.6% of ships use alternative fuels. People worry about the reliability and performance of new tech.
There’s also a lack of global rules. This makes it hard for companies to follow sustainable practices everywhere.
- High initial investment costs for green technologies
- Uncertainty about returns on investment
- Lack of globally harmonised regulations
- Concerns about reliability and performance of new technologies
Despite these challenges, progress is being made. The first bunkering of green methanol-powered ships in 2023 is a step forward. So is the launch of the world’s first carbon-free ammonia fuel network in 2022.
Conclusion: Navigating Towards a Greener Future
The maritime industry is at a critical point in its journey towards sustainability. Shipping is responsible for 2-3% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This has led to a realisation of the need for change.
The International Maritime Organization has set a goal to cut emissions by at least 50% by 2050. This ambitious target aims to start a green revolution at sea.
Summary of Key Innovations
Green shipping corridors and environmental ship design are key strategies for change. The use of alternative fuels like biofuels, hydrogen, and ammonia is expected to reduce emissions. For example, Oldendorff Carriers’ tests with B30 biofuel showed a 20% reduction in carbon emissions.
Electric and hybrid vessels are also making a difference on shorter routes. They significantly lower carbon footprints. Innovations in hull design and lightweight materials improve fuel efficiency. Wind-assist technologies, like rotor sails, use renewable energy to reduce environmental impact.
The IMO’s Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) and mandatory low-sulphur fuels have led to a 40% decrease in carbon intensity. This is a significant achievement between 2008 and 2018.
The Path Forward for the Maritime Industry
The maritime industry’s future is clear but challenging. Stricter emissions rules are pushing for green technologies. The IMO’s 2020 sulphur cap limits fuel sulphur content to 0.5%.
Industry-wide efforts, like the Getting to Zero Coalition, aim for zero-emission vessels by 2030. Companies investing in sustainable shipping improve their brand and appeal to eco-conscious customers. The economic benefits of going green are becoming clear.
The maritime sector’s commitment to a greener future is essential. It’s not just about the environment; it’s a strategic move for success in a changing world.
FAQ
What are green shipping innovations?
Why are green shipping innovations important?
What is LNG and how does it contribute to green shipping?
How are renewable energy sources being used in shipping?
What role does digitalisation play in green shipping?
What are green shipping corridors?
How are major shipping companies implementing green innovations?
What challenges does the shipping industry face in adopting green technologies?
What is the IMO’s role in promoting green shipping?
What are some emerging trends in maritime sustainability?
Source Links
- https://www.ricardo.com/en/news-and-insights/press-releases/2024/ricardo-at-the-helm-of-green-shipping-innovation-for-north-sea-corridor – Ricardo at the helm of green shipping innovation for north sea corridor | Ricardo
- https://www.southampton.ac.uk/research/institutes-centres/centre-for-green-maritime-innovation – Centre for Green Maritime Innovation (cGMI)
- https://www.great.gov.uk/international/investment/sectors/green-shipping/ – Green shipping article great.gov.uk international
- https://humansofglobe.com/green-shipping-innovations-in-sustainable-marine-fuels-and-vessel-design/ – Green Shipping: Innovations in Sustainable Marine Fuels and Vessel Design
- https://www.admiralty.co.uk/decarbonisation/green-shipping-corridor – Green shipping
- https://www.adv-polymer.com/blog/green-shipping – Green Shipping Technology and Achieving Carbon-Zero Today (Updated)
- https://www.export.org.uk/insights/features/five-green-technology-innovations-that-are-transforming-the-shipping-industry/ – Five green technology innovations that are transforming the shipping industry
- https://www.clarksons.com/glossary/what-is-green-shipping/ – What is green shipping? | Clarksons
- https://www.scottish-enterprise.com/learning-zone/case-studies/how-smart-green-shipping-s-fastrig-is-making-shipping-greener – How Smart Green Shipping’s FastRig is making shipping greener
- https://greenshippingproject.com/ – Research network governing environmental improvements in the maritime supply chain – Green Shipping Project
- https://www.rivieramm.com/news-content-hub/news-content-hub/navigating-the-future-innovation-and-digitalisation-can-drive-maritime-sustainability-84051 – Navigating the future: innovation and digitalisation can drive maritime sustainability
- https://www.imo.org/en/MediaCentre/PressBriefings/pages/World-Maritime-Day-2022-.aspx – Environmental technologies in focus on World Maritime Day 2022
- https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/newsroom/news/digitalisation-can-support-shifting – Digitalisation can support shifting to more sustainable transport in Europe
- https://nucleartransportsolutions.com/2024/10/nuclear-ship-embarks-on-pioneering-green-shipping-initiative/ – Nuclear ship embarks on pioneering green shipping initiative – Nuclear Transport Solutions
- https://www.freightamigo.com/shipping-tips/green-shipping-revolutionizing-maritime-industry/ – Green Shipping | Revolutionizing Maritime Industry | FreightAmigo
- https://www.cleantech.com/innovation-through-collaboration-in-the-maritime-sector/ – Innovation Through Collaboration in the Maritime Sector | Cleantech Group
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/256953/uk-singapore-research-partnership-boosts-digital-green/ – UK-Singapore research partnership boosts digital and green shipping | Imperial News | Imperial College London
- https://sinay.ai/en/eco-friendly-shipping-transforming-maritime-sustainability/ – Driving Sustainability in Maritime Transport and Trade
- https://directorstalk.net/green-shipping-corridors-are-transforming-the-maritime-industry – Green shipping corridors are transforming the maritime industry – DirectorsTalk
- https://instituteofsustainabilitystudies.com/insights/lexicon/green-technologies-innovations-opportunities-challenges/ – Green Technologies: Innovations, Opportunities and Challenges
- https://www.polestarglobal.com/resources/green-shipping-corridors/ – Charting a Course Towards Net-Zero: The Promise and Challenges of Green Shipping Corridors – Pole Star Global
- https://www.pdlegal.com.sg/the-current-and-future-opportunities-and-challenges-of-green-shipping-and-sustainability/ – Green Shipping Challenges and Opportunities
- https://www.theenvironmentalblog.org/2024/10/the-future-of-green-shipping-why-it-matters-for-our-planet/ – The Future of Green Shipping: Why It Matters for Our Planet – The Environmental Blog
- https://e-wma.com/green-shipping-the-future-of-sustainable-maritime-transport/ – Green Shipping: The Future of Sustainable Maritime Transport | World Maritime Academy