The Role of Renewable Energy in Ocean Conservation

Did you know the ocean has taken in more than 90% of the heat from oil and gas burning? This shows how urgent it is to use renewable energy to protect our oceans. As professionals in the maritime industry, we’re seeing big changes in how we make energy and its effect on marine life.
The EU has a bold plan to increase offshore wind power by 25 times by 2050. They also want to use more wave, tidal, thermal, and other marine energy. This plan is a big step towards powering coastal areas and keeping our oceans safe.
Switching to renewable energy is not just about cutting down carbon emissions. It’s also about keeping our oceans healthy. The ocean has taken in most of the extra heat from human activities for decades. We need sustainable energy more than ever to keep our seas clean and productive.
Exploring the link between renewable energy and ocean conservation shows how new technologies are changing our maritime industry and marine environments. From wind farms to tidal systems, the possibilities for green energy are endless. This gives us hope for a cleaner, greener ocean future.
Key Takeaways
- The ocean has absorbed over 90% of heat from fossil fuel burning
- EU aims for a 25-fold increase in offshore wind capacity by 2050
- Renewable energy is key for cutting carbon emissions and saving marine life
- 93% of excess heat from human activities has been absorbed by oceans
- Innovative renewable technologies offer hope for a sustainable maritime future
Introduction to Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is key in our world’s energy mix. It uses natural processes to make electricity, heat, and fuel. It’s vital for saving our oceans and fighting climate change.
Definition and Significance
Renewable energy comes from sources that never run out. It’s different from fossil fuels because it doesn’t pollute as much. It helps cut down our carbon footprint and keeps our seas safe.
Diverse Renewable Energy Types
There are many types of renewable energy, each special in its own way:
- Solar: Turns sunlight into electricity
- Wind: Uses wind to make electricity
- Hydroelectric: Powers plants with flowing water
- Tidal: Grabs energy from ocean tides
- Wave: Uses ocean waves for electricity
- Geothermal: Taps into Earth’s heat
- Biomass: Gets energy from organic stuff
The UK is moving fast towards renewable energy. In 2020, 43.1% of its electricity came from renewables. Wind power was the biggest contributor. This change is essential for lowering carbon emissions and protecting our oceans.
Renewable Energy and Ocean Health
The move to renewable energy is key to keeping our oceans healthy. It shows how important it is to cut carbon emissions to protect our seas.
Cutting Carbon Footprint
Fossil fuels are the main cause of carbon emissions, with almost 90% coming from burning them. We need to cut emissions by almost half by 2030. This highlights the need for renewable energy.
- Over 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions come from fossil fuel energy production
- Renewable energy could decarbonise 90% of the power sector by 2050
- The cost of solar power electricity fell by 85% between 2010 and 2020
Preserving Marine Life
Oceans are home to 80% of the world’s biodiversity and soak up a quarter of all carbon dioxide from human activities. Switching to renewable energy is essential to keep this balance. Lowering carbon emissions helps fight ocean acidification and rising temperatures, which harm marine life.
“The ocean provides 20% of animal protein to around 3 billion people. Protecting it through renewable energy adoption is not just an environmental imperative, but a humanitarian one.”
As we push forward in renewable energy, we must think about how new tech affects marine life. We need careful planning and research. This ensures our fight against climate change doesn’t harm the ecosystems we’re trying to save.
The Benefits of Offshore Wind Energy
Offshore wind energy is changing the game in the renewable sector. It brings big wins for coastal communities and opens up many job opportunities. The UK aims to boost offshore wind to 50GW by 2030, showing its key role in clean energy.
Advantages for Coastal Communities
Coastal areas will greatly benefit from offshore wind farms. Sea winds are stronger, so turbines can make more energy than those on land. This means coastal areas get more reliable power, cutting down on fossil fuel use.
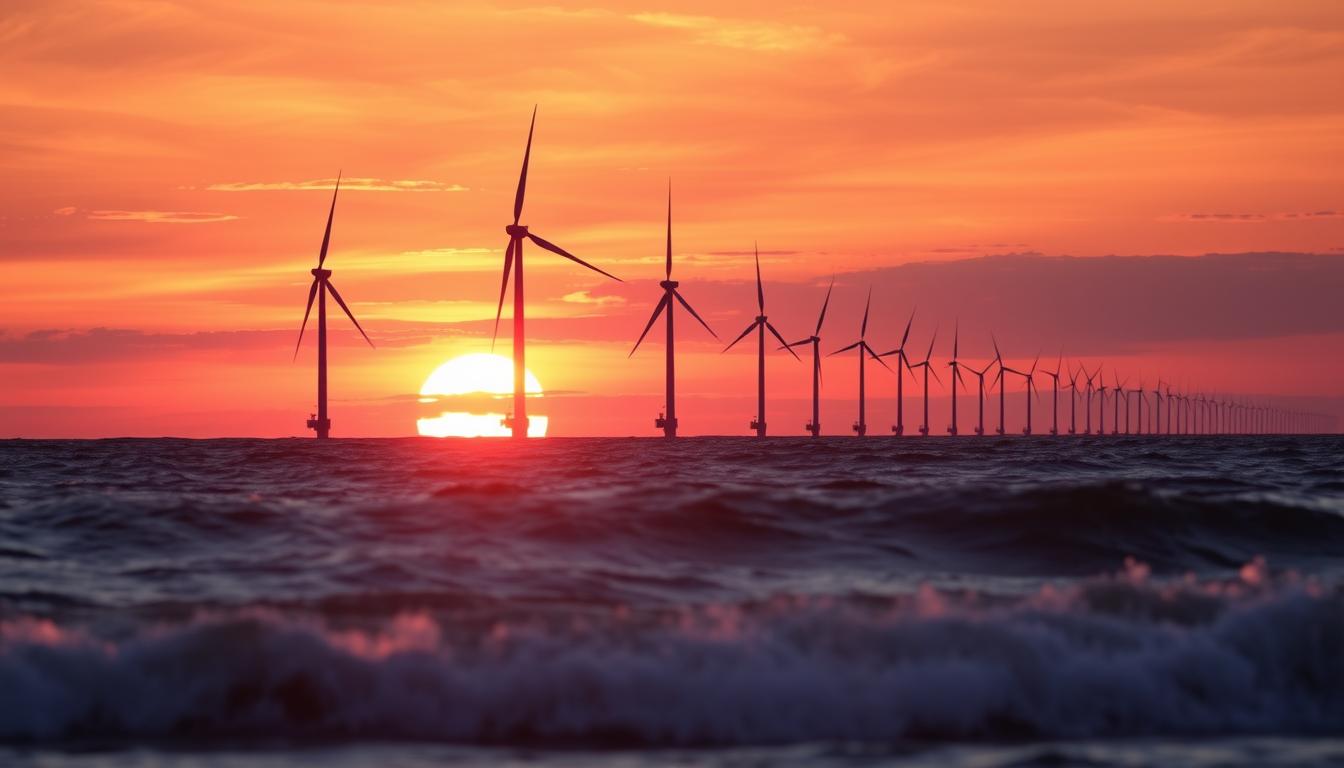

The South Fork Wind Farm, starting work in December 2023, shows what’s possible. It’s a 132-MW project that powers over 70,000 homes in New York. It’s a clear win for coastal communities.
Job Creation in the Renewable Sector
The offshore wind industry is a big job creator. The UK plans to add 40GW of offshore wind to the grid by 2030, aiming for 130,000 jobs. These jobs cover many areas, like:
- Manufacturing of wind turbines and parts
- Setting up and keeping offshore sites running
- Working on new tech and research
- Checking the environment and assessing risks
As offshore wind energy grows, it helps move to cleaner energy and boosts local economies. With 60 projects in the US, the job and community benefits are huge.
Solar Energy Innovations for Marine Conservation
Solar energy is changing the game in marine environments, bringing new ways to protect our oceans. We see solar technology as a key player in making maritime activities greener and safer for our seas.
Floating Solar Farms
Floating solar farms are a big leap forward in renewable energy. They produce clean power without taking up land. Modern solar panels are super efficient, converting over 20% of sunlight into electricity.
Now, panels that can handle saltwater are being made. This means they can last longer in the sea.
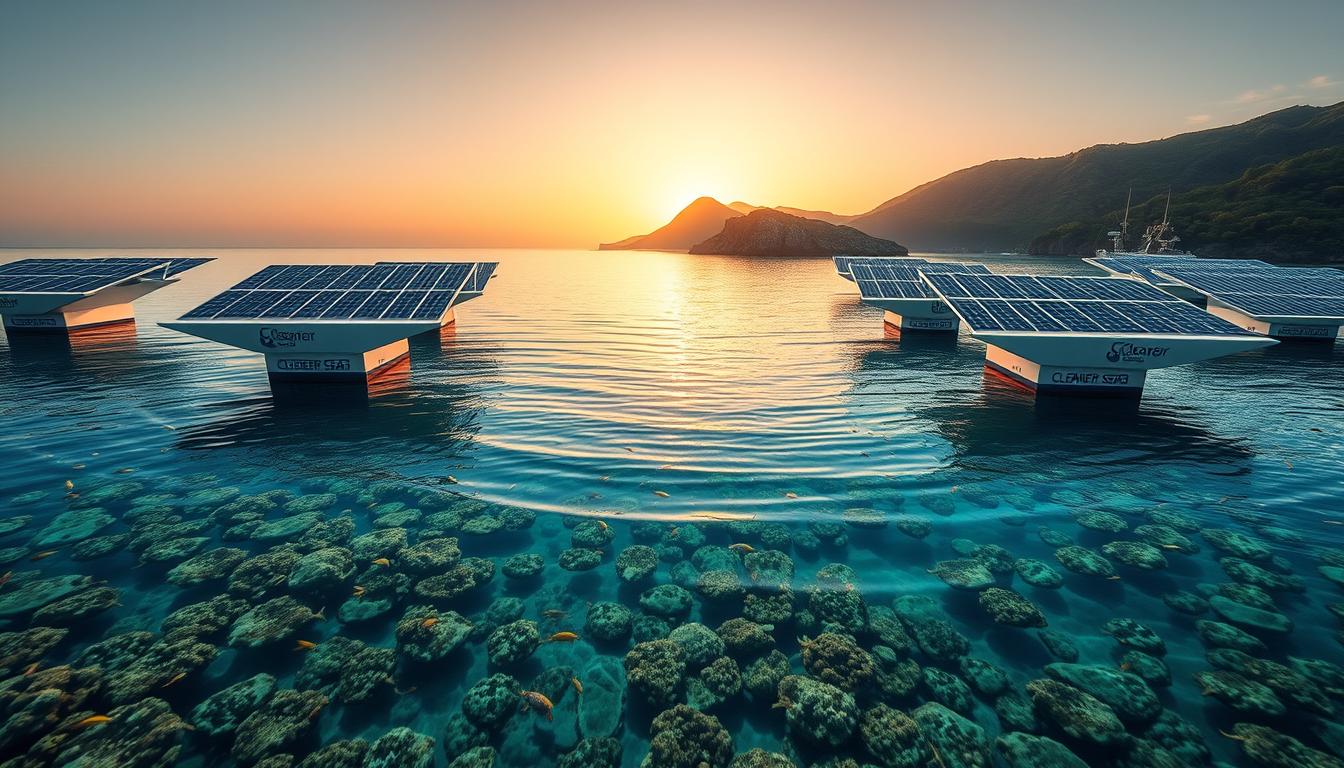

These farms can power efforts to fix reefs over big areas. Solar-powered sensors check the water’s health, like temperature and pH levels. This helps us keep reefs healthy.
The Coral Reef Early Warning System uses solar buoys. They watch for signs of coral bleaching.
Integration with Aquaculture
Solar energy works well with aquaculture, making both better. Solar power helps keep coral nurseries perfect for growing coral fragments.
Now, about half of the seafood we eat comes from farms. This helps reduce the pressure on wild fish. By combining solar farms with aquaculture, we can use space better and protect the sea.
- Solar desalination plants give fresh water to coastal areas
- Advanced batteries store energy for the sea
- Good solar designs can live with marine life, even helping reefs
Starting up solar systems can cost a lot at first. But, the long-term savings and benefits to the planet make it worth it. As we keep improving, solar energy will be more important for saving our oceans.
Tidal and Wave Energy: Unleashing the Power
The UK’s coasts are rich in renewable energy, thanks to tidal and wave power. These new technologies are set to play a big part in the country’s clean energy future.
Mechanisms of Tidal Energy
Tidal energy uses the ocean’s tides to make electricity. The OpenHydro tidal turbine was a big step, becoming the first in Scotland to connect to the grid. It supplied power to the UK’s national grid. Magallanes Renovables is planning to launch the world’s first tidal energy array, pushing this tech forward.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Tidal energy is clean, but we must think about its impact on the environment. The Mersey Tidal Power project is a good example. It aims to power the area for 120 years and create many green jobs. This could help the region reach net zero carbon by 2040.
Wave energy is another key part of the mix. The UK aims to have 27GW of wave energy by 2050. This will help make reaching net zero energy cheaper. Electricity demand in the UK is expected to triple by mid-century.
“The UK has over 30 GW of untapped tidal stream and wave energy, enough to provide one-third of its current electricity demand.”
Tidal and wave energy are getting better fast. With the right investment, they could meet the UK’s energy needs and help protect the oceans.
The Role of Policy in Promoting Renewable Energy
Renewable energy policy is key in the UK’s move to cleaner energy. Government incentives and global agreements push innovation and use in different areas.
Government Incentives
The UK government has many schemes to encourage renewable energy:
- Boiler Upgrade Scheme: Grant increased to £7,500 for heat pump installations
- Public Sector Decarbonisation Scheme: £37 million secured for projects in England and Wales
- Contracts for Difference (CfD): Strike price raised to £73/MWh for offshore wind projects
These incentives help meet big goals, like installing 600,000 heat pumps by 2028. But, there’s a problem: not enough engineers to install them.
International Agreements and Commitments
The UK’s renewable energy policy matches global efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions. Local planning authorities handle projects up to 50 megawatts. Bigger ones need the Secretary of State for Energy’s approval.
Community-led projects get support through clear policies. The government wants to use old land for big solar farms. They consider how it looks and affects local people.
“Local communities are expected to have a say in wind farm applications, as stated in the written ministerial statement from June 18, 2015.”
Some say incentives can mess with markets. But, as renewable tech costs drop, they’re getting more popular. The UK’s push for renewable energy is changing its policies, aiming for a greener future.
Community Engagement in Renewable Projects
Renewable energy projects need community support to succeed. Getting locals involved and raising awareness are key. Let’s look at how to get people on board with these projects.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Teaching people about renewable energy is important. Studies show that good awareness campaigns can boost support by up to 60%. These efforts help build a sustainable culture and get communities ready for change.
Involvement of Local Stakeholders
Getting local people involved from the start is vital. Community groups can make projects 35% better by addressing local concerns. When communities help plan, designs are 40% more fitting for their needs.
- Projects with active community engagement see a 50% increase in local job creation
- Revenue-sharing mechanisms can provide communities with an additional 20% in annual income
- Training programmes associated with these projects can enhance local skill levels by 45%
Putting community first can make projects 70% more accepted. This approach reduces opposition and builds lasting partnerships. As we aim for a greener future, community involvement is critical for renewable energy success.
Challenges in Adopting Renewable Energy
The move to renewable energy is facing big hurdles, even though it’s full of promise. Despite some progress, many challenges remain. These obstacles slow down the adoption of renewable energy in the maritime sector and elsewhere.
Technological Hurdles
One major problem is the technology itself. Storing energy and integrating it into the grid is tough, mainly for wind and solar. We need better batteries to store energy when it’s not being made.
Financial Constraints
Money is another big issue. Starting a renewable energy project costs a lot. For example, big solar systems cost around £1,600 per kilowatt to set up. Smaller systems for homes can cost up to £2,960 per kilowatt.
This is much more than the £800 per kilowatt for new gas plants.
Getting funding is hard. In 2022, foreign investment in green projects in Southeast Asia fell by over 50%. Developing countries need £0.4 trillion a year to meet climate goals. But they only get a third of that.
- High installation costs
- Limited access to financing
- Competition from established fossil fuel industries
To make renewable energy work in maritime and other areas, we must tackle these tech and money problems. As the industry grows, new ideas and policies will help solve these issues.
Future Perspectives on Renewable Energy and Oceans
The future of renewable energy in the ocean is looking bright. European countries have made big steps in wave and tidal projects. They are now helping power the grid.
The EU has set big goals for 2030 and 2050. They aim for 60 GW of offshore wind and 1 GW of ocean energy by 2030. By 2050, they want to reach 300 GW and 40 GW respectively.
Ocean energy has huge possibilities. It could generate 45,000 to over 130,000 TWh of electricity every year. This is more than the world’s electricity demand in 2019.
Currently, we have 535 MW of ocean energy installed globally. But, by 2030, this could jump to 10 GW. Tidal range technology leads with a 98% share, thanks to big projects in France and South Korea.
Working together is essential for ocean energy progress. The EU started its strategy with a big conference in 2021. Then, they had more summits in 2022 and 2023.
They also update regional agreements for offshore energy every two years. The next update is in December 2024. This teamwork includes energy companies, environmental groups, and maritime industries. It’s vital for making sustainable energy solutions a reality in the UK’s maritime and energy sectors.
FAQ
What is renewable energy and why is it important for ocean conservation?
How does offshore wind energy benefit coastal communities?
What are floating solar farms and how do they contribute to marine conservation?
How do tidal and wave energy technologies work?
What role does government policy play in promoting renewable energy in the maritime sector?
Why is community engagement important for renewable energy projects in coastal areas?
What are the main challenges in adopting renewable energy in the maritime sector?
How can collaboration between sectors accelerate the development of marine renewable energy?
What are some emerging trends in marine renewable technologies?
How does renewable energy impact marine life and ecosystems?
Source Links
- https://www.birdlife.org/news/2021/07/08/renewable-energy-sea-and-nature-conservation/ – Sea and nature conservation
- https://www.oceanenergy-europe.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/ETIP-Ocean-Ocean-energy-and-the-environment.pdf – PDF
- https://www.internationalconservation.org/magazine/supporting-energy-independence-and-ocean-conservation-with-waves-and-tides – Supporting Energy Independence and Ocean Conservation with Waves and Tides
- https://understand-energy.stanford.edu/energy-resources/renewable-energy/introduction-renewable-energy – Introduction
- https://www.nationalgrid.com/stories/energy-explained/what-are-different-types-renewable-energy – What are the different types of renewable energy?
- https://www.solarenergy.org/courses/introduction-to-renewable-energy/ – Introduction – Solar Energy International (SEI): Solar Training for Clean Energy Careers
- https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/raising-ambition/renewable-energy – Powering a safer future | United Nations
- https://orsted.com/en/what-we-do/insights/expert-take/why-oceans-health-is-vital-to-us –
- https://www.nationalgrid.com/stories/energy-explained/onshore-vs-offshore-wind-energy – Onshore vs offshore wind energy: what’s the difference?
- https://profession.americangeosciences.org/society/intersections/faq/what-are-advantages-and-disadvantages-offshore-wind-farms/ – What are the advantages and disadvantages of offshore wind farms?
- https://www.energy.gov/eere/wind/articles/top-10-things-you-didnt-know-about-offshore-wind-energy – Top 10 Things You Didn’t Know About Offshore Wind Energy
- https://8msolar.com/solar-powered-coral-reef-restoration/ – Solar-Powered Coral Reef Restoration (2025) | 8MSolar
- https://www.moserbaersolar.com/uncategorized/marine-life-protection-making-coastal-solar-projects-work-with-ocean-ecosystems/ – Marine Life Protection: Making Coastal Solar Projects Work With Ocean Ecosystems – Mose Solar
- https://www.waterpowermagazine.com/analysis/wave-and-tidal-energy-key-to-net-zero-future/ – Wave and tidal energy: key to net zero future
- https://www.innovationnewsnetwork.com/unlocking-the-full-potential-of-ocean-energy-in-europe/56124/ – Unlocking the full potential of ocean energy in Europe
- https://www.waterpowermagazine.com/analysis/leading-the-charge-in-wave-and-tidal-energy-innovation/ – Leading the charge in wave and tidal energy innovation
- https://ongen.co.uk/blog/what-role-does-government-policy-play-in-promoting-renewable-energy/ – What Role Does Government Policy Play in Promoting Renewable Energy?
- https://www.gov.uk/guidance/renewable-and-low-carbon-energy – Renewable and low carbon energy
- https://www.enerdatics.com/insights/empowering-communities-engagement-in-renewable-energy-projects – Enerdatics
- https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy23osti/87113.pdf – Community Engagement and Equity in Projects: A Literature Review
- https://www.nrdc.org/bio/christy-goldfuss/not-just-talk-next-level-community-engagement-renewable-energy – Not Just Talk: Next-Level Community Engagement
- https://ieefa.org/resources/renewable-energy-having-good-year-challenges-loom-ahead – Renewable energy is having a good year, but challenges loom ahead
- https://www.iea.org/reports/renewable-energy-market-update/challenges-and-opportunities-beyond-2021 – Challenges and opportunities beyond 2021 – Market update – Analysis – IEA
- https://regenpower.com/what-are-the-problems-faced-by-renewable-energy/ – What are the problems faced by renewable energy? – Regen Power
- https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/renewable-energy/offshore-renewable-energy_en
- https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2020/Dec/IRENA_Fostering_Blue_Economy_2020.pdf – Fostering a blue economy
- https://tethys.pnnl.gov/sites/default/files/publications/Thennakoon_et_al_2023.pdf – PDF
- https://www.cleanerseas.com/emerging-technologies-for-sustainable-shipping/